Embark on a scientific odyssey with our comprehensive biology transcription and translation worksheet answers. Delve into the intricacies of gene expression, where DNA’s blueprint unravels into the symphony of life. Understand the processes that transform genetic information into the proteins that shape our world.
This guide unravels the complexities of transcription and translation, illuminating the roles of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the intricate dance of life. Prepare to witness the elegance of genetic code and explore the profound implications of mutations on our genetic tapestry.
Transcription Process: Biology Transcription And Translation Worksheet Answers
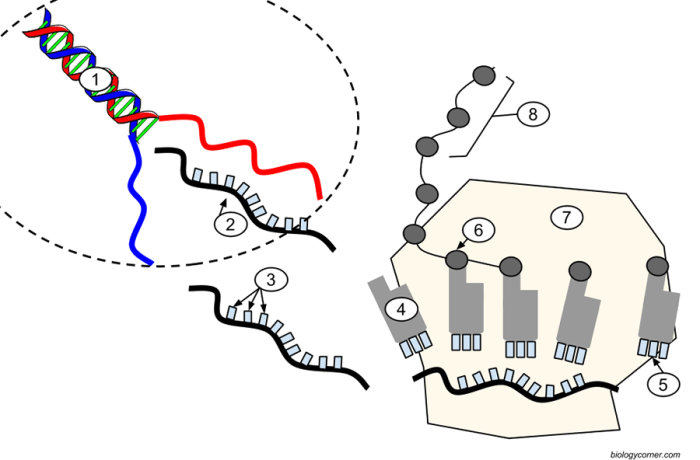
Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied into RNA. It is carried out by RNA polymerase, an enzyme that binds to DNA and uses it as a template to create a complementary RNA molecule.
The mRNA transcript is then released from the DNA template and travels to the cytoplasm, where it will be translated into a protein.
An example of a DNA sequence and its corresponding mRNA transcript is shown below:
- DNA: ATCGTACGTATCG
- mRNA: UAGCAUGCAUAGC
Translation Process
Translation is the process by which mRNA is translated into a protein. It is carried out by ribosomes, which are large, complex structures that bind to mRNA and use it as a template to create a polypeptide chain.
The tRNA molecule carries the amino acid to the ribosome, where it is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
An example of an mRNA sequence and its corresponding polypeptide product is shown below:
- mRNA: AUGCCAUGCAUAGC
- Polypeptide: Met-His-His-Ser
Genetic Code

The genetic code is a set of rules that determines how the sequence of nucleotides in DNA is translated into the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
The genetic code is redundant, meaning that there are multiple codons that code for the same amino acid. It is also universal, meaning that the same genetic code is used by all living organisms.
A table showing the codons and their corresponding amino acids is shown below:
| Codon | Amino Acid |
|---|---|
| UUU | Phe |
| UUC | Phe |
| UUA | Leu |
| UUG | Leu |
| … | … |
Mutations and Transcription/Translation Errors
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can affect transcription and translation, leading to the production of non-functional proteins.
There are different types of mutations, including point mutations, insertions, and deletions.
Point mutations are the most common type of mutation. They involve the substitution of one nucleotide for another.
Insertions and deletions are mutations that involve the addition or removal of nucleotides from the DNA sequence.
Mutations can have a variety of consequences, depending on their location and the type of mutation.
Some mutations are silent, meaning that they do not have any effect on the protein product.
Other mutations can lead to the production of non-functional proteins, which can cause genetic diseases.
An example of a genetic disease caused by a transcription error is sickle cell anemia.
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene. This mutation results in the production of a defective beta-globin protein, which leads to the formation of sickle-shaped red blood cells.
Applications of Transcription and Translation

Transcription and translation are essential processes for all living organisms.
These processes are used to produce proteins, which are the building blocks of cells and tissues.
Transcription and translation are also used to produce vaccines and genetically modified organisms.
Vaccines are used to protect people from diseases. Vaccines are made by using transcription and translation to produce weakened or inactivated forms of viruses or bacteria.
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are organisms that have had their DNA altered. GMOs are used to improve crop yields, create new medicines, and produce biofuels.
FAQ Guide
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA double helix, synthesizes a complementary RNA strand using one DNA strand as a template, and elongates the RNA strand in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
How do tRNA molecules function in translation?
tRNA molecules carry specific amino acids and recognize the corresponding codons on mRNA through their anticodons. They bring the correct amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
What is the genetic code?
The genetic code is a set of rules that dictate the relationship between the sequence of codons in mRNA and the sequence of amino acids in proteins.