As pull on the earth’s crust stretching rock takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authoritative academic tone, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. The intricate interplay between crustal stretching and rock formations unravels before our very eyes, promising a journey through the geological forces that have shaped our planet.
Crustal stretching, a fundamental process in shaping the Earth’s surface, occurs when tectonic forces exert a pull on the Earth’s crust, causing it to thin and extend. This phenomenon has left an indelible mark on our planet, from the formation of rift valleys to the development of new ocean basins.
In this exploration, we delve into the mechanisms driving crustal stretching, its impact on rock formations, and its profound geological implications.
Understanding the Stretching of the Earth’s Crust

Crustal stretching refers to the process by which the Earth’s crust thins and extends horizontally. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface features and has significant geological implications.
Crustal stretching occurs when two or more tectonic plates move away from each other, causing the crust between them to stretch and thin. This process is often associated with the formation of rift valleys, the precursors to new ocean basins.
Examples of regions where crustal stretching has occurred include the East African Rift System, the Red Sea, and the Gulf of California.
Factors contributing to crustal stretching include the movement of tectonic plates, the presence of magma chambers beneath the crust, and the density differences between the crust and the underlying mantle.
The Role of Pull Forces in Crustal Stretching
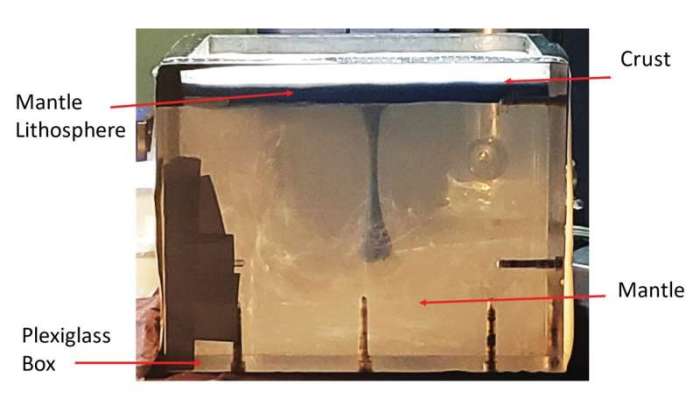

Various pull forces can stretch the Earth’s crust, including:
- Plate Tectonics:The movement of tectonic plates away from each other exerts a pulling force on the crust, causing it to stretch.
- Magma Intrusion:The upward movement of magma into the crust can create pressure that stretches the overlying crust.
- Density Differences:The crust is less dense than the underlying mantle, and this density difference can cause the crust to be pulled down into the mantle, stretching it in the process.
Impacts of Crustal Stretching on Rock Formations

Crustal stretching can have a profound impact on the structure and composition of rocks:
- Thinning:Crustal stretching causes the crust to thin, which can lead to the formation of new rocks.
- Folding:The stretching of the crust can cause rocks to fold and buckle.
- Faulting:Crustal stretching can create faults, which are fractures in the crust.
Different types of rock formations can result from crustal stretching, including rift valleys, grabens, and horsts.
Geological Implications of Crustal Stretching: Pull On The Earth’s Crust Stretching Rock
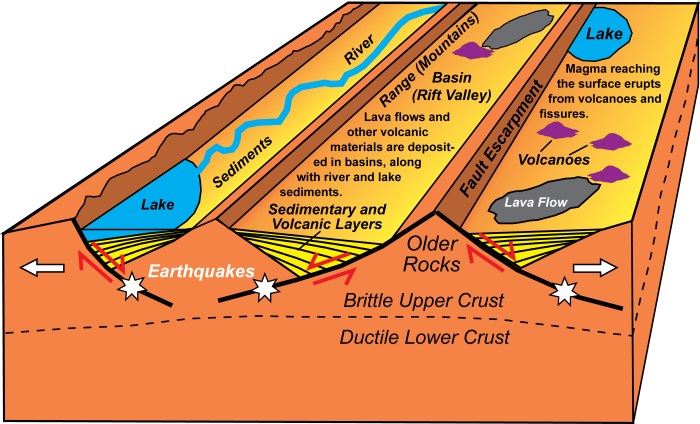
Crustal stretching has significant geological implications:
- Formation of Rift Valleys and Ocean Basins:Crustal stretching can lead to the formation of rift valleys, which are long, narrow depressions in the Earth’s surface. Over time, rift valleys can evolve into ocean basins as the crust continues to stretch and thin.
- Earthquakes and Volcanic Activity:Crustal stretching can trigger earthquakes and volcanic activity. Earthquakes occur when the stretched crust ruptures, while volcanic activity can occur when magma rises through the stretched crust.
- Shaping of Earth’s Surface Features:Crustal stretching plays a role in shaping the Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, valleys, and ocean basins.
FAQ Resource
What are the primary forces responsible for crustal stretching?
Crustal stretching is primarily driven by tectonic forces, including divergent plate boundaries, where plates move away from each other, and extensional forces within plates.
How does crustal stretching affect rock formations?
Crustal stretching can lead to the formation of various rock formations, such as thinned crust, metamorphic rocks, and rift-related volcanic rocks.
What are the geological implications of crustal stretching?
Crustal stretching has significant geological implications, including the formation of rift valleys, the development of new ocean basins, and the triggering of earthquakes and volcanic activity.