Welcome to our comprehensive physio epithelial tissues review worksheet, a valuable resource for understanding the fundamental concepts and applications of these specialized tissues. Delve into the fascinating world of physio epithelial tissues, exploring their intricate structure, diverse functions, and clinical relevance.
Our worksheet provides a structured and engaging learning experience, empowering you with a thorough understanding of this essential topic.
Throughout this worksheet, we will delve into the key characteristics, classification, functions, and clinical significance of physio epithelial tissues. We will examine their structural organization, regeneration mechanisms, and the role they play in various medical conditions. By the end of this worksheet, you will possess a deep understanding of physio epithelial tissues, their vital contributions to bodily functions, and their implications in healthcare.
Overview of Physio Epithelial Tissues
Physio epithelial tissues, also known as covering and lining tissues, are specialized tissues that cover the surfaces of the body and line its internal cavities and organs. They provide protection, regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, and facilitate various physiological functions.
Key Characteristics and Functions
Physio epithelial tissues are characterized by their:
- Closely packed cells with minimal extracellular matrix
- Polarity, with distinct apical and basolateral surfaces
- Specialized cell junctions that maintain tissue integrity
Their functions include:
- Protection against mechanical, chemical, and biological insults
- Regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance through selective permeability
- Secretion and absorption of substances
Classification of Physio Epithelial Tissues
Physio epithelial tissues are classified based on their structure and function. The following table summarizes the main types:
| Type | Location | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple squamous epithelium | Blood vessels, alveoli, Bowman’s capsule | Single layer of flat, thin cells | Gas exchange, filtration |
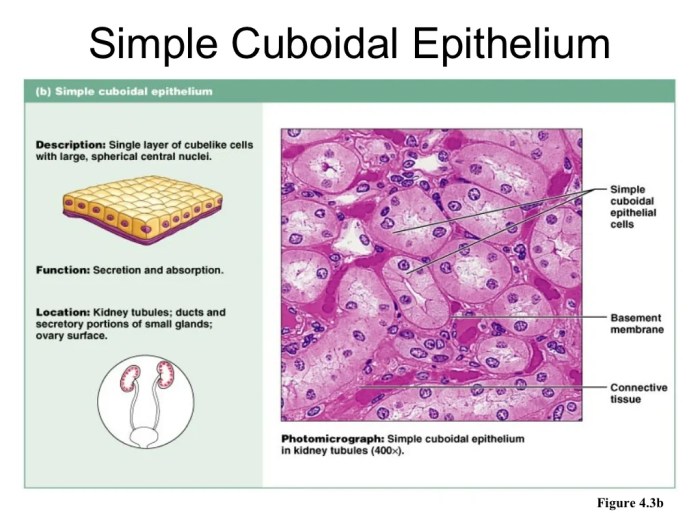
| Simple cuboidal epithelium | Kidney tubules, ducts | Single layer of cube-shaped cells | Secretion, absorption |
| Simple columnar epithelium | Intestine, stomach | Single layer of tall, column-shaped cells | Absorption, secretion |
| Pseudostratified columnar epithelium | Trachea, bronchi | Single layer of cells, but not all reach the free surface | Secretion, protection |
| Stratified squamous epithelium | Skin, esophagus | Multiple layers of cells, with superficial cells being flat | Protection |
| Transitional epithelium | Urinary bladder | Cells change shape depending on bladder volume | Accommodation of stretching |
Functions of Physio Epithelial Tissues
Physio epithelial tissues perform a wide range of functions, including:
Protection
Epithelial tissues form physical barriers that protect underlying tissues from external hazards, such as pathogens, toxins, and mechanical damage.
Secretion
Certain epithelial tissues secrete substances such as enzymes, hormones, and mucus. These secretions aid in digestion, lubrication, and protection.
Absorption
Epithelial tissues lining the digestive tract and respiratory system facilitate the absorption of nutrients, gases, and other substances.
Excretion
Epithelial tissues in the kidneys and sweat glands excrete waste products and excess fluids from the body.
Structure and Organization of Physio Epithelial Tissues: Physio Epithelial Tissues Review Worksheet
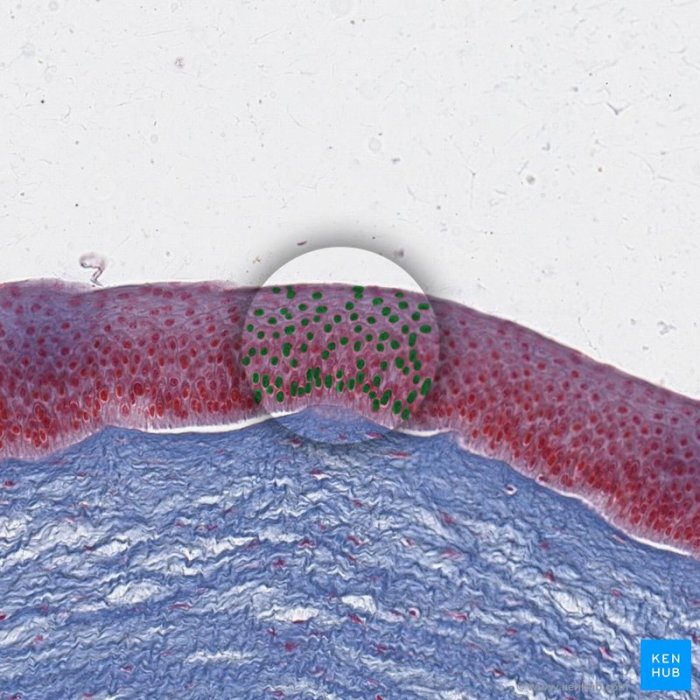
Physio epithelial tissues are highly organized, with a specific arrangement of cells and extracellular matrix.
Cell Arrangement, Physio epithelial tissues review worksheet
Epithelial cells are arranged in a single layer (simple epithelium) or multiple layers (stratified epithelium). The shape of the cells varies depending on the tissue’s function.
Extracellular Matrix
The extracellular matrix is a thin layer of glycoproteins and proteoglycans that surrounds and connects epithelial cells. It provides structural support and facilitates cell-cell communication.
Cell Junctions
Epithelial cells are connected by specialized cell junctions, including:
- Tight junctions: Prevent leakage between cells
- Adherens junctions: Maintain cell-cell adhesion
- Gap junctions: Allow direct communication between cells
Regeneration and Repair of Physio Epithelial Tissues
Physio epithelial tissues have a high capacity for regeneration and repair. This is facilitated by:
Stem Cells
Stem cells reside within epithelial tissues and can differentiate into specialized epithelial cells to replace damaged or lost cells.
Cell Proliferation
Existing epithelial cells can undergo cell division to increase the number of cells and repair damaged areas.
Clinical Significance of Physio Epithelial Tissues
Physio epithelial tissues play a crucial role in various medical conditions:
Wound Healing
Epithelial tissues regenerate to cover wounds and restore the skin’s integrity.
Cancer Development
Abnormal changes in epithelial tissues can lead to the development of carcinomas, the most common type of cancer.
Immune Responses
Epithelial tissues are involved in immune responses by secreting cytokines and interacting with immune cells.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the primary functions of physio epithelial tissues?
Physio epithelial tissues perform various essential functions, including protection, secretion, absorption, and excretion. They act as barriers against external threats, produce and release substances, facilitate the uptake of nutrients, and eliminate waste products.
How are physio epithelial tissues classified?
Physio epithelial tissues are classified based on their structure and function. The main types include simple epithelium, stratified epithelium, pseudostratified epithelium, and transitional epithelium. Each type exhibits unique characteristics and is adapted to specific locations and functions within the body.
What is the role of physio epithelial tissues in wound healing?
Physio epithelial tissues play a crucial role in wound healing. They form the protective layer over the wound site, preventing infection and promoting tissue repair. The basal layer of epithelial cells proliferates and migrates to cover the wound, restoring the integrity of the skin or other affected tissues.