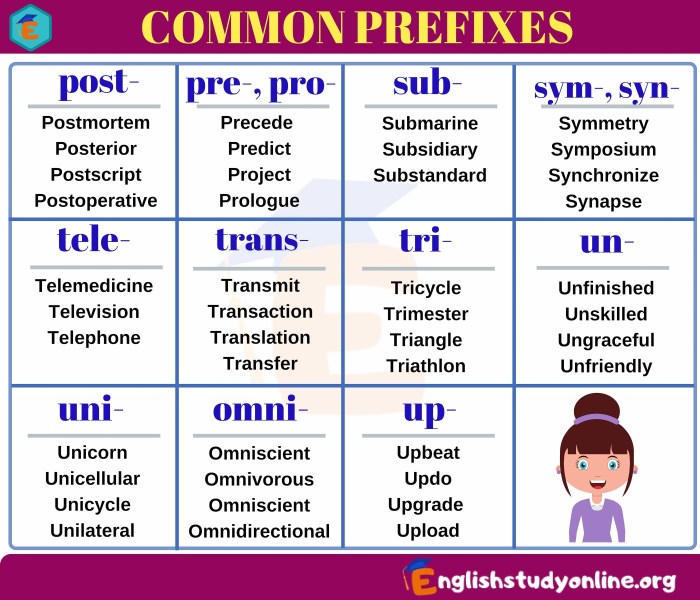
Suffix with hypn to mean sleep-inducing – Suffixes with “hypn” possess the remarkable ability to induce sleep, opening up a fascinating chapter in pharmacology and medicine. This suffix, rooted in the Greek word for “sleep,” has played a pivotal role in the development of sleep-inducing substances that have transformed the treatment of sleep disorders.
Throughout history, the “hypn” suffix has adorned words describing sleep-inducing effects, providing a rich tapestry of linguistic evidence for its enduring association with slumber.
Etymology and Historical Usage: Suffix With Hypn To Mean Sleep-inducing
The suffix “hypn” is derived from the Greek word “hypnos,” which means “sleep.” Historically, the suffix has been used to denote substances that induce sleep or promote relaxation.
Examples of words using the “hypn” suffix include “hypnosis,” which refers to a state of trance or sleep-like relaxation, and “hypnotic,” which describes substances or techniques that induce sleep.
Pharmacological Mechanisms
Substances with the “hypn” suffix generally work by interacting with specific receptors in the brain, particularly those involved in the regulation of sleep-wake cycles.
- Benzodiazepines:Bind to GABA receptors, enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission and promoting relaxation and sleep.
- Non-benzodiazepine hypnotics:Bind to different receptors, such as orexin receptors, to reduce wakefulness and promote sleep.
Therapeutic Applications
Sleep-inducing substances with the “hypn” suffix are primarily used to treat insomnia and other sleep disorders.
- Benzodiazepines:Used for short-term treatment of severe insomnia due to their rapid onset and potent sedative effects.
- Non-benzodiazepine hypnotics:Preferred for long-term treatment of insomnia due to their lower risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Potential side effects of sleep-inducing substances with the “hypn” suffix include:
- Drowsiness
- Impaired coordination
- Memory impairment
- Dependence
- Respiratory depression (in high doses)
Caution should be exercised when using these substances, particularly in the elderly and those with underlying medical conditions.
Comparison to Other Sleep-Inducing Agents, Suffix with hypn to mean sleep-inducing
Sleep-inducing substances with the “hypn” suffix differ from other classes of sleep-inducing agents in several ways:
- Mechanism of action:Hypnotics generally target specific receptors in the brain, while other agents may have different mechanisms, such as blocking histamine receptors (antihistamines) or stimulating melatonin production (melatonin agonists).
- Efficacy:Hypnotics are generally more effective in inducing sleep than other agents, but they may also have more side effects.
- Side effect profile:Hypnotics can cause drowsiness, impaired coordination, and memory impairment, while other agents may have different side effects, such as dry mouth (antihistamines) or nightmares (melatonin agonists).
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research focuses on developing new sleep-inducing substances with improved efficacy, reduced side effects, and novel mechanisms of action.
- Orexin antagonists:Targeting orexin receptors, which are involved in wakefulness, may lead to more effective and less addictive sleep-inducing agents.
- Dual-acting agents:Combining the mechanisms of action of different sleep-inducing agents may improve efficacy and reduce side effects.
- Personalized medicine:Tailoring sleep-inducing treatment to individual patient profiles may enhance outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
FAQ Explained
What is the etymology of the suffix “hypn”?
The suffix “hypn” originates from the Greek word “hypnos,” meaning “sleep.”
How do substances with the suffix “hypn” induce sleep?
These substances interact with specific neurotransmitter systems in the brain, promoting relaxation and inhibiting arousal.
What are some common therapeutic applications of sleep-inducing substances with the suffix “hypn”?
They are used to treat insomnia, anxiety-related sleep disorders, and other conditions that impair sleep.